Deleting an element in a linked list →
Now, let us progress with looking at slightly more complicated operations. In our previous post, we saw find operation that required us to traverse the list, but we needed to keep track of only one element while traversing - just match the element with the item we are trying to find and see if we found. But in some cases, we may have to keep track of more than one element - this is because we need to rearrange the pointers. Suppose, we have the following linked list with 4 elements:
19 -> 49 -> 21 -> 17 -> NULL
(0) (1) (2) (3)
and we are asked to delete the element at index 2 (its data being 21). We not only need to keep track of the current element to be deleted, we need to remember the previous element (in this case the one at index 1 with value 49) because this would point to 17 after deleting the one at index 2. Specifically, after the deletion, the linked list would look like this:
19 -> 49 -> 17 -> NULL
(0) (1) (2)
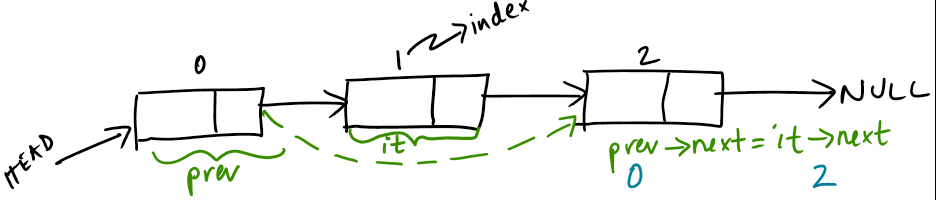
In order to do this algorithmically, we keep track of two nodes, the current one (iterator denoted it in code below) and the previous node (denoted prev in code fragment below). As we traverse the list looking for the item at index, we decrement the index and once we find it, we rearrange the pointers - in particular, we set delete the node and attach prev to the rest of the linked list that followed the deleted node (i.e., the list pointed to by the deleted node’s next). Besides, we also need to handle cases when the index is ‘0’, i.e. we are trying to delete the first node or if the given index does not exist at all. A visual sketch is given below, followed by the method to perform the deletion.
void LinkedList::delete_at_index (int index) {
if (index >= this->length || index < 0)
throw out_of_range("Index out of range for the linkedlist");
Node *it = this->head;
Node *prev = NULL;
while (it != NULL) {
cout << ":: index: " << index << ":";
if (index == 0)
break;
index--;
prev = it;
it = it->next;
cout << " (prev->data, it->data) : " << prev->data << ", " << it->data << endl;
}
if (prev == NULL) {
this->head = it->next;
delete it;
}
else {
prev->next = it->next;
delete it;
}
}